“My academic program is perfect and needs no improvements” – said no student ever. Instead, we students often think about how we can improve our performance and protect against potential setbacks. The solution? SWOT analysis.
What is a SWOT analysis?
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique that examines your situation through four critical lenses: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. While it may seem simple, this framework helps you make unbiased evaluations of:
- Your academic performance
- Career planning
- Project strategies
- Study methods
- Extracurricular activities
Importance of a SWOT Analysis
- It provides space for reflection and aspiration: SWOT analysis gives you dedicated time to both address concerns and explore possibilities. You’re creating space to dream, evaluate, and plan before taking action.
- It forces you to define variables: Instead of jumping straight into planning, you first take inventory of your assets and challenges. This process helps you develop strategies that use your strengths while addressing weaknesses.
- It helps identify mitigating factors: As you recognize weaknesses and threats, you can better account for them in your planning, improving your chances of success.
- It creates a written record: As your academic journey progresses, you can track changes, mark off accomplished goals, and add new considerations.
Parts of a SWOT Analysis
Let’s explore each component with relevant academic examples:
Strengths

- What are you naturally good at?
- What skills have you developed?
- What resources do you have access to? Example strengths:
- Strong research abilities
- Effective time management
- Access to good study resources
- Positive relationships with professors
I have discovered that by identifying and capitalizing on your strengths, you can build a solid foundation for growth. You can also use those strengths in other areas that might need additional support, for instance, increasing customer satisfaction
Weaknesses
- Where do you need improvement?
- What resources do you lack?
- What do others identify as your weaknesses? Example weaknesses:
- Test anxiety
- Procrastination tendencies
- Limited networking connections
- Gaps in prerequisite knowledge
Opportunities
- What positive external factors could you leverage?
- What trends could benefit you?
- What resources are newly available? Example opportunities:
- New research positions opening
- Growing demand in your field
- Available mentorship programs
- Study abroad options
Threats
- What obstacles might you face?
- What competition exists?
- What external factors could cause problems? Example threats:
- Increasing program requirements
- Strong competition for internships
- Schedule conflicts
- Financial constraints
External and Internal Factors of a SWOT Analysis
Think of a SWOT analysis as looking at your academic life through two different lenses: factors you can control (internal) and factors you can’t control (external). Let’s break these down in a way that makes sense for students.
Internal Factors (Things Within Your Control)
Internal factors are like your personal toolkit – the skills, habits, and resources that belong to you. In a SWOT analysis, your strengths and weaknesses are internal factors because you can directly influence them.
Strengths Examples (Internal)
- Your study habits and time management skills
- Knowledge of specific subjects
- Personal motivation and work ethic
- Note-taking abilities
- Public speaking skills
- Research capabilities
- Language proficiencies
- Technical skills (like coding or data analysis)
Weaknesses Examples (Internal)
- Tendency to procrastinate
- Test anxiety
- Difficulty with certain subjects
- Poor organization skills
- Limited experience with group projects
- Struggles with academic writing
- Time management challenges
- Gaps in prerequisite knowledge
External Factors (Things Outside Your Control)
External factors are like the weather – they affect your situation, but you can’t directly change them. In a SWOT analysis, opportunities and threats are external factors that you need to navigate rather than control.
Opportunities Examples (External)
- New research programs at your school
- Upcoming internship positions
- Available scholarships
- Growing job market in your field
- Study abroad programs
- Mentor availability
- New technology resources on campus
- Industry connections through professors
Threats Examples (External)
- Increasing course requirements
- Competition for program admission
- Changes in degree requirements
- Limited class availability
- Economic conditions affecting job prospects
- Reduced funding for research
- Technology changes in your field
- Schedule conflicts with required courses
How do you write a good SWOT analysis?
Based on my experience helping students, here are the key steps to creating an effective SWOT analysis:
- Dowload a good SWOT analysis templates Don’t start from scratch! Use a template to organize your thoughts. Think of it like having a study guide – it gives you a clear structure to follow. You can find free SWOT templates online or create a simple four-quadrant grid on paper.
Pro tip: Keep it simple. A basic four-box grid works perfectly – just label your boxes Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- Arrange each section into a table with four quadrants Just like organizing your notes for different subjects, give each component its own clear space. This visual organization helps you see connections between different areas and keeps your analysis clear and focused.
- Identify your objective Before diving in, get crystal clear about what you’re analyzing. Are you evaluating:
- Your current semester performance?
- A specific class?
- Your study habits?
- A group project?
- Your career preparation?
Being specific helps you focus your analysis and make it more useful.
- Identify your strengths Think about what you’re genuinely good at. Ask yourself:
- What do your professors consistently praise you for?
- Which subjects come naturally to you?
- What study techniques work best for you?
- What unique skills or experiences do you bring to your studies?
Pro tip: Get input from classmates, professors, or academic advisors. Sometimes others see strengths we don’t recognize in ourselves.
- Identify your weaknesses This isn’t about being hard on yourself – it’s about honest self-improvement. Consider:
- Which subjects or tasks do you struggle with?
- What feedback do you consistently receive about areas for improvement?
- What habits might be holding you back?
- Where do you need more support or resources?
Pro tip: Look at your past academic feedback and grades. They often reveal patterns that can help identify areas needing work. customer feedback report
- Consider your opportunities This is your chance to think big! Look for:
- New academic programs or courses being offered
- Research opportunities in your department
- Upcoming internship possibilities
- Study abroad options
- Mentorship programs
- New technology or resources available
- Growing career fields related to your major
Pro tip: Stay informed about your department’s newsletters and announcements – they often contain valuable opportunities.
- Contemplate your threats Think about potential obstacles to your success:
- Challenging upcoming courses
- Competition for programs or opportunities
- Time management challenges
- Financial constraints
- Changes in degree requirements
- Work-life balance issues
Pro tip: Remember that identifying threats isn’t about worrying – it’s about preparing. Once you know what challenges you might face, you can plan for them
SWOT Analysis Examples
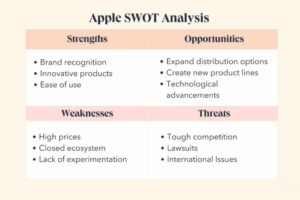
Apple’s SWOT analysis
Here’s how I would conduct a SWOT analysis on Apple.
Strengths
First off, strengths. While Apple has many strengths, in my opinion the top three are:
- Brand recognition.
- Innovative products.
- Ease of use.
Apple’s brand is undeniably strong, and its business is considered the most valuable in the world. Since it’s easily recognized, Apple can produce new products and almost ensure a certain degree of success by virtue of the brand name itself.
Apple’s highly innovative products are often at the forefront of the industry. One thing that sets Apple apart from the competition is its product inter-connectivity. For instance, as an Apple user, I can easily sync my iPhone and iPad together and access all of my photos, contacts, and apps no matter which device I am using.
Lastly, customers enjoy how easy it is to use Apple’s products. With a sleek and simple design, each product is developed so that most people can quickly learn how to use them.
Weaknesses
Next, let’s look at three of Apple’s weaknesses:
- High prices.
- Closed ecosystem.
- Lack of experimentation.
While the high prices don’t deter Apple’s middle- and upper-class customer base, they do hinder Apple’s ability to reach a lower-class demographic.
Apple also suffers from its own exclusivity. Apple controls all its services and products in-house, and while many customers become loyal brand advocates for this reason, it means all burdens fall on Apple employees.
Ultimately, Apple’s tight control over who distributes its products limits its market reach.
Lastly, Apple is held to a high standard when it comes to creating and distributing products. Apple’s brand carries a high level of prestige. That level of recognition inhibits Apple from taking risks and experimenting freely with new products that could fail.
Opportunities
Now, let’s take a look at opportunities for Apple. It was easy to recognize opportunities for improvement, once I considered Apple’s weaknesses. Here’s a list of three that I came up with:
- Expand distribution options.
- Create new product lines.
- Technological advancement.
One of Apple’s biggest weaknesses is its distribution network, which, in the name of exclusivity, remains relatively small. If Apple expanded its network and enabled third-party businesses to sell its products, it could reach more people globally, while alleviating some of the stress currently put on in-house employees.
There are also plenty of opportunities for Apple to create new products. Apple could consider creating more affordable products to reach a larger demographic, or spreading out into new industries — Apple self-driving cars, perhaps?
Finally, Apple could continue advancing its products’ technology. Apple can take existing products and refine them, ensuring each product offers as many unique features as possible
Threats
Finally, I looked at threats to Apple because believe it or not, they do exist. Here are three of Apple’s biggest threats according to their customers (me):
- Tough competition.
- International issues.
Apple isn’t the only innovative tech company out there, and it continues to face tough competition from Samsung, Google, and other major forces. In fact, Samsung sold more smartphones than Apple did in Q1 of 2022, shipping 17 million more units than Apple and holding 24% of the market share.
Many of Apple’s weaknesses hinder Apple’s ability to compete with the tech corporations that have more freedom to experiment, or that don’t operate in a closed ecosystem.
A second threat to Apple is lawsuits. Apple has faced plenty of lawsuits, particularly between Apple and Samsung. These lawsuits interfere with Apple’s reputable image and could steer some customers to purchase elsewhere.
Finally, Apple needs to improve its reach internationally. If Apple can’t compete globally the way Samsung or Google can, it risks falling behind in the industry.